Russia, located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, has always had a unique position in the global political landscape. But have you ever wondered why Russia seems to be a prisoner of geography? Despite its vast expanse and abundant resources, the country has faced numerous challenges throughout history. In this article, we will explore the geographical factors that have shaped Russia’s destiny and continue to influence its politics, economy, and foreign relations.
The unique geography of Russia
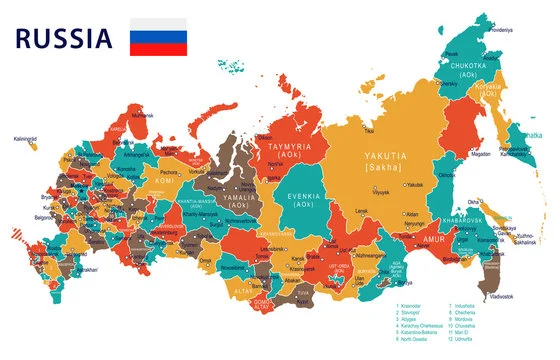
Russia’s geography presents a complex set of obstacles and opportunities. From its frozen Arctic territories to its sprawling Siberian landscapes, the country is a land of extremes. It spans eleven time zones and covers one-eighth of the Earth’s inhabited land area. This vast expanse gives Russia the advantage of abundant natural resources, from oil and gas reserves to vast forests and mineral deposits. However, it also poses significant challenges in terms of governance, infrastructure development, and maintaining control over such a vast territory.
Russia’s geography is characterized by diverse climates and terrains. The country experiences extreme temperature variations, with freezing winters and scorching summers. It is home to the world’s largest forest, the taiga, as well as vast plains, mountains, and rivers. These diverse landscapes have shaped Russia’s regional power dynamics and influenced its historical development.
Influence of geography on Russian history and culture
Russia’s geography has played a crucial role in shaping its history and culture. The vastness of its territory has made it difficult to govern and unify the country. Throughout its history, Russia has faced the challenge of maintaining control over its regions and managing the relationships between its diverse ethnic and cultural groups.
The country’s geography has also influenced its historical expansion and conquests. The vast plains of Eastern Europe and Central Asia have provided Russia with natural pathways for expansion, leading to the incorporation of territories such as Crimea, Ukraine, and the Caucasus region. The conquest of these territories has had a profound impact on Russia’s national identity and geopolitical ambitions.
Natural resources and their impact on Russia’s economy
Russia’s vast reserves of natural resources have played a significant role in its economy. The country is one of the world’s largest producers and exporters of oil, gas, and minerals. These resources have been a major source of wealth for Russia and have helped sustain its economy. However, the heavy reliance on resource extraction has also made Russia vulnerable to fluctuations in global commodity prices.
The geographical distribution of resources within Russia has also influenced the country’s economic development. Many of the resource-rich regions, such as Siberia and the Far East, are located in remote and inhospitable areas. The development of infrastructure and transportation networks to exploit these resources has been a significant challenge for Russia.

Challenges and opportunities posed by Russia’s geography
Russia’s geography presents both challenges and opportunities for the country. The vastness of its territory and the diversity of its landscapes make governance and infrastructure development difficult. The harsh climate and remote locations of many regions pose challenges for economic development and human settlement. However, this geography also provides opportunities for resource extraction, agriculture, and tourism.
The country’s geography also poses challenges for national security. Russia’s long borders with numerous countries make it vulnerable to external threats and territorial disputes. The proximity to Europe and Asia has also shaped Russia’s geopolitical position and influenced its foreign policy.
Russia’s geopolitical role and its geographic implications
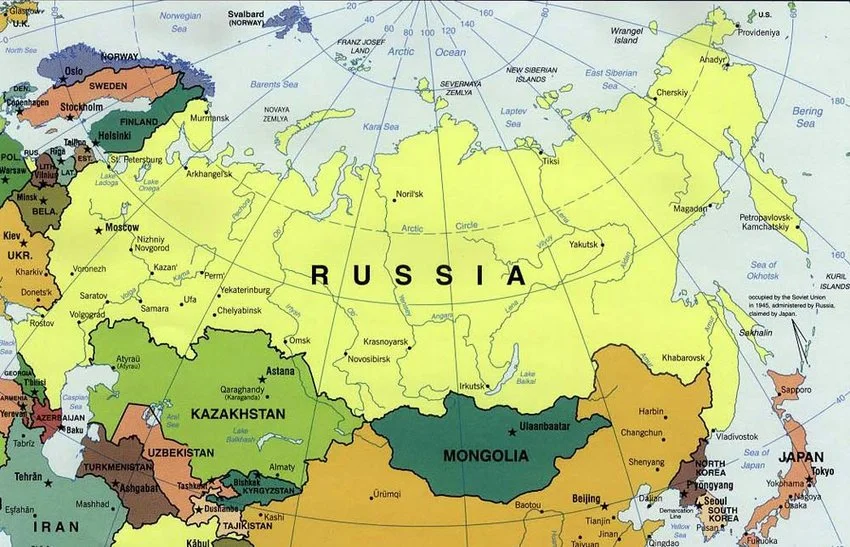
Russia’s geography has positioned it as a key player in global geopolitics. Its location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia gives it a unique strategic advantage. The country has historically been seen as a bridge between East and West and has played a significant role in shaping the balance of power in Eurasia.
The geographical implications of Russia’s location have influenced its relationships with neighboring countries and global powers. The country’s proximity to Europe has led to historical tensions and conflicts, such as the Napoleonic Wars and the Cold War. The Arctic territories of Russia have also become a focal point of geopolitical competition due to the region’s vast oil and gas reserves and the opening of new shipping routes as a result of melting ice caps.
The impact of geography on Russia’s relations with neighboring countries
Russia’s geography has a profound impact on its relations with neighboring countries. The country shares borders with fourteen countries, including China, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, and Finland. These borders have been the source of both cooperation and conflict throughout Russia’s history.
The proximity to Europe has led to a complex relationship with the European Union and NATO. Russia’s historical expansion into Eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union states has created tensions, particularly with countries that aspire to join Western institutions. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine is a prime example of how geography can shape geopolitical dynamics and influence regional stability.
Strategies used by Russia to overcome its geographic constraints
Despite the challenges posed by its geography, Russia has implemented various strategies to overcome its constraints and leverage its advantages. The country has invested in infrastructure development, such as the Trans-Siberian Railway and the Northern Sea Route, to improve connectivity and facilitate resource extraction.
Russia has also pursued a robust military strategy to protect its territorial integrity and maintain influence in its neighboring regions. The country’s military presence in the Arctic and Crimea is a reflection of its strategic priorities and the importance of geography in its defense and security doctrines.
Lessons that can be learned from Russia’s experience with geographic determinism
Russia’s experience with geographic determinism offers valuable lessons for other countries facing similar challenges. The country’s history demonstrates the importance of effective governance, infrastructure development, and regional cooperation in overcoming geographic constraints.
The case of Russia also highlights the need for a balanced approach to resource extraction and economic development. Overreliance on natural resources can lead to economic vulnerability and hinder diversification efforts. Investing in education, innovation, and sustainable development can help countries reduce their dependence on finite resources.
The ongoing significance of geography in shaping Russia’s destiny
In conclusion, Russia’s geography has played a pivotal role in shaping its destiny. The country’s vast expanse, diverse landscapes, and abundant resources have presented both opportunities and challenges throughout its history. Understanding the influence of geography on Russia’s politics, economy, and foreign relations is crucial for gaining insights into the country’s decision-making and aspirations.
As Russia continues to navigate the complexities of its geography, it will need to adapt and innovate to overcome its constraints and leverage its advantages. The ongoing significance of geography in shaping Russia’s destiny cannot be underestimated, and its impact will continue to shape the country’s past, present, and future.
If you found this exploration into Russia’s geographical intricacies enlightening, we invite you to delve into our detailed analysis of the United States’ geography. Discover how the United States leverages its own diverse landscapes, strategic locations, and natural resources to maintain its position as a global superpower. Join us in understanding another fascinating aspect of how geography can shape the destiny of nations.