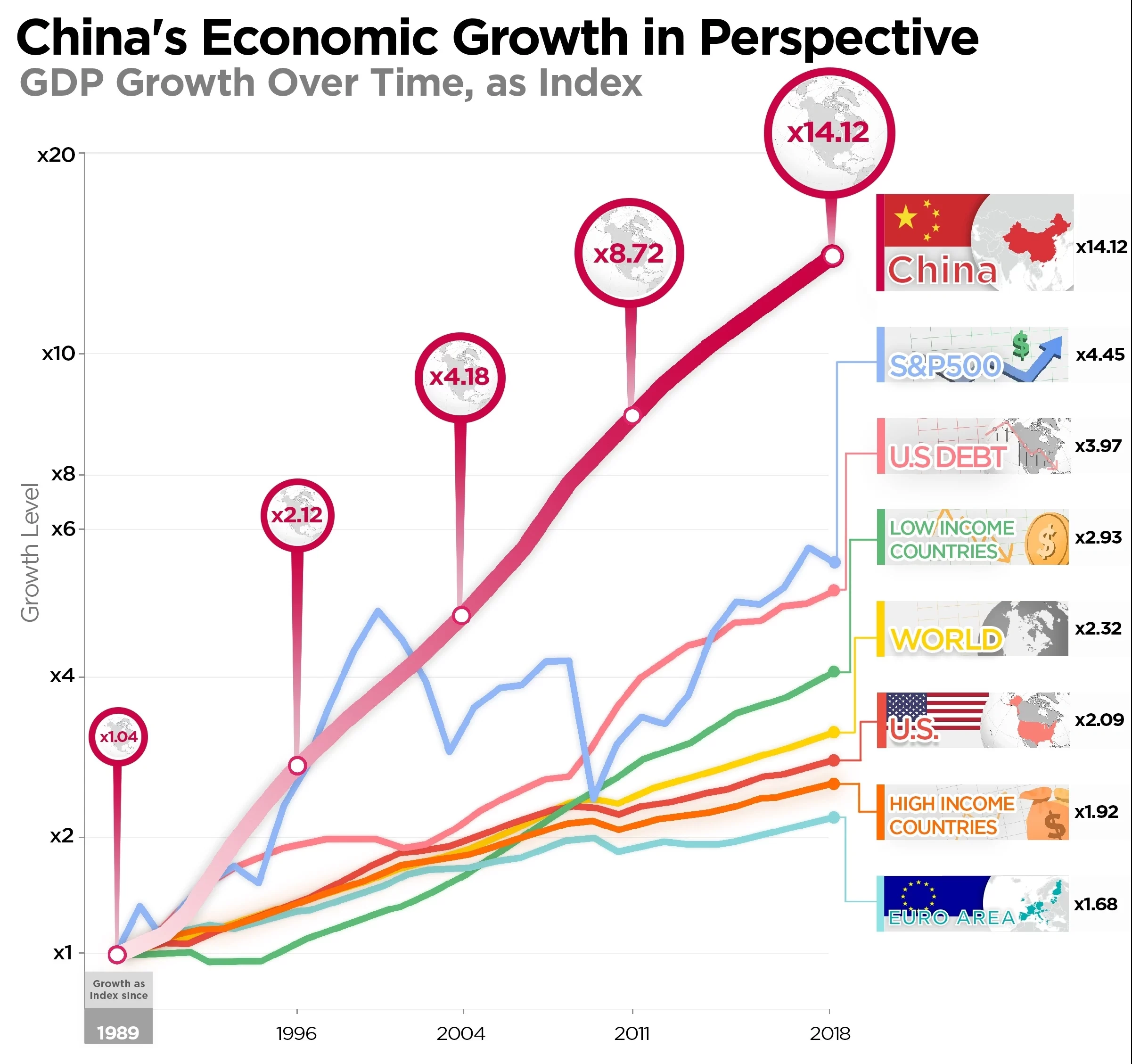
China’s Economic Rise: Over the past few decades, China has experienced a remarkable economic and geopolitical growth, positioning itself as a global powerhouse. From a state-controlled economy to becoming the world’s second-largest economy, China’s rise is undeniable. The economic growth of China has been fueled by various factors, including its massive population, extensive manufacturing capabilities, and aggressive infrastructure development. With a focus on exports and attracting foreign investments, China has emerged as a major player in international trade. The country’s rapid industrialization and technological advancements have significantly contributed to its economic success.
China’s geopolitical growth is also worth noting. The nation has been actively strengthening its global influence through strategic investments, diplomatic efforts, and ambitious infrastructure projects like the Belt and Road Initiative. As China’s economic and military might expand, it is redefining the dynamics of international relations and challenging the established order.
In this article, we will explore the key factors driving China’s rise, the implications of its economic and geopolitical growth, and the potential challenges it may face in sustaining this rapid growth trajectory. Join us as we delve into the fascinating story of China’s transformation and its impact on the world stage.
Historical Context of China’s Rise
China’s rise as an economic and geopolitical power did not happen overnight. It has a rich historical context that laid the foundation for its current success. For centuries, China was one of the world’s largest economies, known for its advancements in science, technology, and trade. However, in the 19th and early 20th centuries, China went through a period of decline and instability due to internal conflicts, foreign invasions, and the impact of the Opium Wars.
It was not until the late 1970s when China implemented economic reforms under the leadership of Deng Xiaoping that the country began its journey towards rapid economic growth. Deng Xiaoping’s policies introduced market-oriented reforms, opening up China to foreign investments and allowing for the development of a more market-driven economy. This shift from a centrally planned economy to a socialist market economy laid the groundwork for China’s economic rise.
Economic Growth and Development in China
China’s economic growth over the past few decades has been nothing short of spectacular. The country’s gross domestic product (GDP) has grown at an average annual rate of around 10%, far outpacing most other major economies. China has transitioned from an agrarian society to an industrial powerhouse, with manufacturing and exports playing a key role in its economic success.
One of the key factors driving China’s economic growth is its massive population. With over 1.4 billion people, China has a vast labor force, which has been a significant advantage in attracting foreign investments and powering its manufacturing sector. The country has become a global manufacturing hub, producing a wide range of goods for both domestic consumption and export.
China’s aggressive infrastructure development has also been instrumental in its economic growth. The country has invested heavily in building an extensive network of roads, railways, ports, and airports, connecting its cities and regions. This infrastructure development has not only facilitated domestic trade and economic activities but has also enhanced China’s global connectivity and trade links.
Key Factors Contributing to China’s Economic Rise
Several key factors have contributed to China’s economic rise. First and foremost is its export-oriented approach. China has positioned itself as the “factory of the world,” with its low-cost manufacturing capabilities and efficient supply chains. The country has successfully attracted multinational corporations to set up production facilities in China, taking advantage of its large labor force and favorable business environment.
Additionally, China has invested heavily in research and development (R&D) and technological innovation. The country has made significant strides in areas such as telecommunications, renewable energy, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology. China’s emphasis on innovation has propelled its economic growth and helped it move up the value chain in various industries.
Furthermore, China’s domestic market has played a crucial role in its economic rise. As the middle class continues to grow, consumer spending has increased, driving demand for a wide range of products and services. This expanding domestic market has provided a strong foundation for China’s economic growth and has also made it less reliant on exports.
China’s Role in the Global Economy
China’s rise has had a profound impact on the global economy. It has become a major player in international trade, with its exports accounting for a significant portion of the world’s total trade volume. China’s manufacturing capabilities and competitive pricing have made its products highly sought after in global markets.
Moreover, China has actively pursued free trade agreements and economic partnerships with countries around the world. The country has established itself as a key player in regional trade blocs such as the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC). China’s participation in these trade agreements has further enhanced its economic integration with the global economy.
China’s economic rise has also brought about a shift in the global balance of power. As the world’s second-largest economy, China’s influence in global financial institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank has increased. The country has been advocating for reforms in these institutions to better reflect the changing global economic landscape.

Geopolitical Implications of China’s Rise
China’s economic growth has been closely intertwined with its geopolitical ambitions. As its economy has expanded, so has its influence on the world stage. China has been actively pursuing a more assertive foreign policy, seeking to protect its interests and shape the global order to align with its own objectives.
One of the key manifestations of China’s geopolitical ambitions is the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). Launched in 2013, this ambitious infrastructure project aims to connect China with Europe, Asia, and Africa through a network of roads, railways, ports, and other infrastructure projects. The BRI has been hailed as a new Silk Road, promoting trade and economic cooperation between China and participating countries. However, it has also raised concerns about China’s growing influence and debt sustainability in recipient countries.
China’s military modernization has also been a significant aspect of its geopolitical rise. The country has been investing heavily in its defense capabilities, expanding its naval fleet, developing advanced military technologies, and asserting territorial claims in the South China Sea. China’s military buildup has raised concerns among neighboring countries and has led to increased tensions in the region.
China’s Belt and Road Initiative
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is one of the most ambitious infrastructure projects in modern history. It aims to connect China with Europe, Asia, and Africa through a network of roads, railways, ports, and other infrastructure projects. The BRI encompasses more than 70 countries and covers approximately 65% of the world’s population. It is expected to facilitate trade, promote economic growth, and enhance connectivity between participating countries.
The BRI has the potential to reshape global trade patterns and strengthen China’s economic and geopolitical influence. By investing in infrastructure projects, China is not only creating new trade routes but also establishing closer ties with participating countries. However, the BRI is not without its challenges. Concerns have been raised about the financial sustainability of the projects, the environmental impact, and the potential for debt dependency among participating countries.
Challenges and Potential Risks for China’s Growth
Despite its impressive economic growth, China faces several challenges and potential risks that could hinder its continued rise. One of the key challenges is the need to transition from an export-driven economy to one that is more reliant on domestic consumption and innovation. China’s heavy dependence on exports makes it vulnerable to global economic downturns and trade tensions.
Another challenge is the need to address income inequality and promote inclusive growth. While China’s economic rise has lifted millions of people out of poverty, it has also resulted in a significant wealth gap. The government will need to implement policies to ensure that the benefits of economic growth are distributed more equitably across society.
Furthermore, China’s rapid industrialization and urbanization have taken a toll on the environment. The country faces significant environmental challenges, including air and water pollution, deforestation, and climate change. Addressing these environmental issues is crucial for China’s sustainable development and long-term economic growth.
Future Prospects and Implications of China’s Rise
China’s rise is expected to have far-reaching implications for the global economy and international relations. As the country’s economy continues to grow, it will likely play an even more prominent role in shaping global trade patterns, investment flows, and technological advancements.
China’s rise also presents both opportunities and challenges for other countries. On one hand, China’s growing middle class and expanding domestic market offer significant opportunities for businesses and investors around the world. On the other hand, the rise of China could also lead to increased competition in certain industries and geopolitical tensions in the Asia-Pacific region.
The future prospects of China’s rise will depend on how the country manages its economic and geopolitical challenges. China will need to continue implementing structural reforms, promoting innovation, and addressing social and environmental issues. Additionally, China’s ability to navigate geopolitical tensions and build constructive relationships with other countries will be key to its long-term success.

China’s Impact on the World Stage
China’s rise as an economic and geopolitical powerhouse has had a profound impact on the world stage. The country’s rapid economic growth, driven by factors such as its massive population, extensive manufacturing capabilities, and aggressive infrastructure development, has positioned it as a major player in international trade. China’s economic success has been accompanied by a more assertive foreign policy, as evidenced by initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative and its military modernization.
While China’s rise presents opportunities for economic cooperation and development, it also raises concerns about the country’s growing influence and potential risks associated with its rapid growth trajectory. As China continues to navigate its economic and geopolitical challenges, its future prospects will have significant implications for the global economy and international relations.
In conclusion, China’s transformation from a state-controlled economy to the world’s second-largest economy has been an extraordinary journey. Its rise as an economic and geopolitical power will continue to shape the world in the years to come, and it is essential for policymakers, businesses, and individuals to understand the implications and challenges that come with it. China’s rise is a story of ambition, innovation, and the pursuit of global influence, and its impact on the world stage is undeniable.
If you found this exploration into China’s economic ascent enlightening, we invite you to delve deeper into the intricacies of global diplomacy and cooperation by reading our article about the United Nations. There, we uncover the pivotal role of international collaborations in fostering peace, security, and development worldwide.




